债券收益率上升,但风险何在?
在经历了多年的低收益之后, bonds are offering higher yields that may be appealing to investors regardless of their risk tolerance. 虽然债券可以在任何投资组合中发挥作用, they can be a mainstay for retirees looking for stability and income, and near-retirees might consider shifting some assets into bonds in preparation for retirement.

Bonds are generally considered to have lower risk than stocks — one good reason to own them — but they are not without risk. 事实上,债券面临多重风险. 在考虑下面的简短解释时, keep in mind that coupon rate refers to the interest paid on the face value of a bond, whereas yield refers to the return to the investor based on the purchase price. A bond purchased for less than face value will have a higher yield than the coupon rate, and a bond purchased for more than face value will have a lower yield than the coupon rate.
利率风险(或市场风险) ——利率上升的风险, making the coupon rate on an existing bond less appealing because new bonds offer higher rates. This typically lowers the value of a bond on the secondary market, but it would not change the yield for a bond purchased at issue and held to maturity. As the Federal Reserve has rapidly raised rates to combat inflation, the potential resale value of existing bonds has plummeted. 然而, 利率可能正接近峰值, which potentially could make it a more opportune time to purchase bonds. If interest rates drop, the value of a bond will typically increase.
时间风险 — the risk that longer-term bonds will be more sensitive to changes in interest rates. Duration is stated in years and based on the bond’s maturity date as well as other factors. A 1% increase in interest rates typically will decrease a bond’s value on the secondary market by 1% for each year of duration. 例如, a bond with a duration of seven years can be expected to lose 7% of its value on the secondary market.
机会风险(或持有期风险) — the risk that you will not be able to take advantage of a potentially better 投资. 债券期限越长, the greater the risk that a more attractive 投资 might arise or other events might negatively impact your bond 投资.
通胀风险 — the risk that the yield on a bond will not keep up with the rate of inflation. This might be of special concern in the current environment, but high inflation is the reason that the Fed has been raising interest rates. If inflation cools, bonds with today’s higher yields could outpace inflation going forward.
书信书信
Bond ratings in descending order of creditworthiness as judged by the three best-known rating agencies (shaded ratings are considered non-投资 grade)
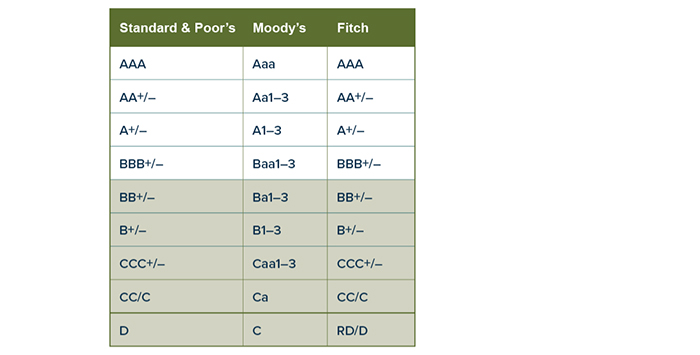
注:标准 & Poor’s and Fitch Ratings use the symbols + and – to denote the upper and lower ranges of ratings from AA to CCC; Moody’s uses the numbers 1, 2, 3表示上面, 中间, Aa - Caa范围较低.
调用风险 — the risk that an issuer will redeem the bond when interest rates are falling in order to issue new bonds at lower rates. Investors can avoid this risk by purchasing non-callable bonds.
信用风险(或违约风险) — the risk that the bond issuer is unable to make promised interest payments and/or return principal upon maturity. Credit-rating agencies analyze this risk and issue ratings that reflect their assessment. 评级较高的债券被认为是“投资级”.” Lower-rated bonds, commonly called “junk bonds,” are non-投资 grade. They generally offer higher yields and are considered speculative with higher credit risks.
一些评级较低的债券可能有保险, 所以债券有两个评级, 一个是保证金,一个是保险公司. Bond insurance adds a potential layer of protection if an issuer defaults, but it is only as good as the insurer’s credit quality and ability to pay. An investor should not buy bonds based solely on the insurance.
The principal value of bonds may fluctuate with market conditions. Bonds redeemed prior to maturity may be worth more or less than their original cost. Investments seeking to achieve higher yields also involve a higher degree of risk.